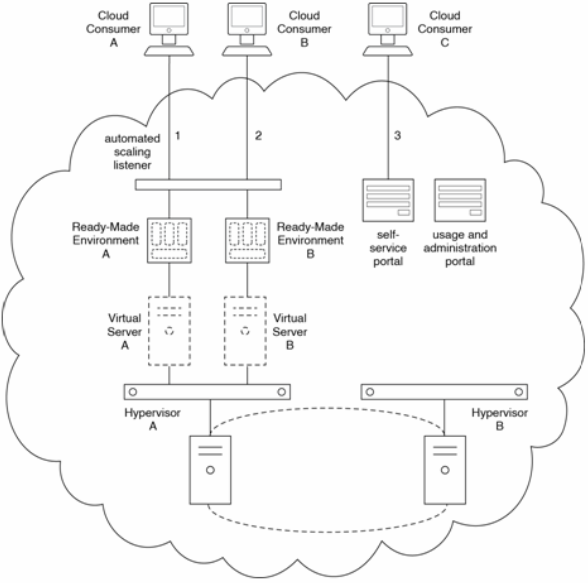
Ready-Made Environment A is hosted by Virtual Server A and Ready-Made Environments is hosted by Virtual Server B. Virtual Servers A and B are hosted by Hypervisor A, which is part of a hypervisor cluster. An automated scaling listener intercepts cloud consumer requests and automatically invokes the on-demand generation of additional instances of ready-made environments, as required.
A self-service portal and a usage and administration portal are also available to cloud consumers. The self-service portal can be used to request the provisioning of a new ready- made environment. Any cloud consumer that has already had a ready-made environment provisioned can configure and view information about that ready-made environment via the usage and administration portal.
Cloud Consumer A accesses Ready-Made Environment A to work on the development of a new cloud service (1). Cloud Consumer B accesses Ready-Made Environment B to test a recently completed application comprised of three cloud services (2). Cloud Consumer C accesses the self-service portal to request the creation of a new ready-made environment
(3).
The cloud provider is required to perform an emergency maintenance outage on a cloud storage device used by all ready-made environments. The unplanned outage takes two hours. During this period, Cloud Consumers A and B are unable to access Ready-Made
Environments A and B and Cloud Consumer C receives an error when submitting a request to create a new ready-made environment.
After the maintenance outage is over, Cloud Consumers A and B encounter the following problems:
-> Cloud Consumer A is unable to recover session data that was kept in memory for an extended period, prior to the time of the outage.
-> Cloud Consumer B has no access to Virtual Server B, which was moved to
Hypervisor B during the maintenance outage. When Cloud Consumer B attempts to ping Virtual Server B, the request times out.
Even though Cloud Consumer C is able to lo
- A. A combination of the Load Balanced Virtual Server Instances and Synchronized Operating State patterns can be applied to establish a system capable of deferring state across multiple cloud storage devices, each located on a different virtual server. The Elastic Disk Provisioning pattern can be applied to persist virtual server configuration data across hypervisors so that connectivity is preserved whenever a virtual server is relocated to a different hypervisor. The Zero Downtime pattern can be a
- B. The Elastic Disk Provisioning and Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering patterns can be applied to establish a cloud architecture that supports a set of cloud storage devices, each with different tiers that cloud consumers can choose to scale to The Synchronized Operating State pattern can be applied in combination with the Hypervisor Clustering pattern to avoid further virtual server and ready-made environment connectivity problems. The Redundant Storage pattern can be applied so that if a clou
- C. The Service State Management pattern can be applied to establish a system that can persist session data in a database. The Persistent Virtual Network Configuration pattern can be applied to centralize the configuration data necessary for virtual servers to remain accessible after they have been relocated to different hypervisors. The Storage Maintenance Window pattern can be applied to establish a system that allows cloud storage devices to be maintained without causing outages.
- D. None of the above.
Answer : C
Cloud Service A is installed on Virtual Server A and the database it accesses is located on
- A. The Resource Reservation pattern can be applied to ensure that Virtual Servers A and B are not accessed by any cloud consumers other than Organization A, thereby enabling their respective capacity to be maximized. A second hypervisor can be implemented and the Synchronized Operating State pattern can be applied to emulate the usage of the resource cluster mechanism with the two hypervisors. This will prevent Cloud Service A from being affected if one of the hypervisors fails. The Service State M
- B. The Elastic Resource Capacity pattern can be applied to enable resources to be assigned to the virtual servers dynamically. The Hypervisor Clustering pattern can be applied to avoid jeopardizing the availability of Cloud Service A when its underlying hypervisor fails. The Multipath Resource Access pattern can be applied to establish an alternative path to Cloud Storage Device A. Cloud Service A can then be designed to access Cloud Storage Device A via the alternative path whenever access via the
- C. The Elastic Resource Capacity pattern can be applied to enable resources to be assigned to the virtual servers dynamically. The Resource Pooling pattern can be applied to allow Hypervisor A to be part of a larger hypervisor pool. The Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering pattern can be applied to allow Cloud Service A to access Cloud Storage Device A via different tiers.
- D. None of the above.
Answer : B
Cloud Service A requires access to Cloud Storage Device A, which contains LUNs A and
B. Cloud Service A is hosted by Virtual Server A, which resides on Hypervisor A on
- A. Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering, Pay-as-You-Go. Self-Provisioning
- B. Service Load Balancing, Pay-as-You-Go, Multipath Resource Access
- C. Intra-Storage Device Vertical Data Tiering, Usage Monitoring, Centralized Remote Administration
- D. None of the above.
Answer : D
Virtual Server A and Virtual Server B are hosted by Hypervisor A, which resides on
- A. The Resource Reservation pattern can be applied to protect the Cloud Service A implementation via the use of a logical network perimeter. The Workload Distribution pattern can be applied to introduce a load balancing system for Cloud Service A. The Zero Downtime pattern can be applied to establish a system that allows Cloud Service A to be constantly available, even during maintenance outages.
- B.
- C. The Non-Disruptive Service Relocation pattern can be applied to establish a system that uses live VM migration to move the virtual server hosting Cloud Service A to a new physical server without allowing any downtime. The Dynamic Scalability pattern can be applied to establish a system whereby multiple instances of Cloud Service A can be created and an automated scaling listener can be used to redirect concurrent requests to the Cloud Service A instances. The Non-Disruptive Service Relocation pa
- D. None of the above.
Answer : C
Cloud Service A is hosted by Virtual Server A, which is hosted by Hypervisor A on Physical
- A. The Intra-Storage Device Vertical Data Tiering pattern can be applied to enable dynamic scaling between Cloud Storage Devices A, B and C. The Dynamic Failure Detection and Recovery pattern can be applied to establish a resilient watchdog system that is able to respond dynamically to prevent data loss. The Service State Management pattern can be applied to keep a copy of the data in Cloud Storage Devices A, B and C during the maintenance outages.
- B. The Cross-Storage Device Vertical Tiering pattern can be applied to enable dynamic scaling between Cloud Storage Devices A, B and C. The Redundant Storage pattern can be applied by designating Cloud Storage Device D as the secondary storage to which Organization A's data can be replicated. In order to prevent planned or unplanned outages from affecting Organization A's data access, the Storage Maintenance Window pattern can be applied to replicate the data in Cloud Storage Device D for retrieval
- C. The Load Balanced Virtual Switches pattern can be applied to increase the bandwidth of Physical Server A so that data processing problems within Cloud Storage Device A can be prevented. The Non-Disruptive Service Relocation pattern can be applied to automatically relocate Cloud Storage Device A to Physical Server B so that data access is not interrupted. The Storage Maintenance Window pattern can be applied to replicate the data in Cloud Storage Device D for retrieval before the outages begin.
- D. None of the above.
Answer : B

