Your network contains a single Active Directory site.
You plan to deploy 1,000 new computers that will run Windows 7 Enterprise. The new computers have Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) network adapters.
You need to plan the deployment of the new computers to meet the following requirements:
Support 50 simultaneous installations of Windows 7
Minimize the impact of network operations during the deployment of the new computers
Minimize the amount of time required to install Windows 7 on the new computers
What should you include in your plan?
- A. Deploy the Windows Deployment Services (WDS) server role. Configure the IP Helper tables on all routers.
- B. Deploy the Windows Deployment Services (WDS) server role. Configure each WDS server by using native mode.
- C. Deploy the Windows Deployment Services (WDS) server role and the Transport Server feature. Configure the Transport Server to use a custom network profile.
- D. Deploy the Windows Deployment Services (WDS) server role and the Transport Server feature. Configure the Transport Server to use a static multicast address range.
Answer : D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc726564%28WS.10%29.aspx http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc725964%28WS.10%29.aspx
WDS Multicast Server -
Updated: November 21, 2007 -
Applies To: Windows Server 2008 -
The multicast server deploys an image to a large number of client computers concurrently without overburdening the network. When you create a multicast transmission for an image, the data is sent over the network only once, which can drastically reduce the network bandwidth that is used.
Using Transport Server -
Updated: May 8, 2008 -
Applies To: Windows Server 2008 -
This topic only applies to Windows Server 2008. If you have Windows Server 2008 R2, see
Configuring Transport Server.
You have two options when installing the Windows Deployment Services role in Windows
Server 2008. You can install both the Deployment Server and Transport Server role services (which is the default) or you can install only the Transport Server role service. The second configuration is for advanced scenarios, such as environments without Active
Directory Domain Services (AD DS), Domain Name System (DNS), or Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP). You can configure Transport Server to enable you to boot from the network using Pre-Boot Execution Environment (PXE) and Trivial File Transfer
Protocol (TFTP), a multicast server, or both. Note that Transport Server does not contain or support the Windows Deployment Services image store.
Configure how to obtain IP addresses. If multiple servers are using multicast functionality on a network (Transport Server, Deployment Server, or another solution), it is important that each server is configured so that the multicast IP addresses do not collide. Otherwise, you may encounter excessive traffic when you enable multicasting. Note that each
Windows Deployment Services server will have the same default range. To work around this issue, specify static ranges that do not overlap to ensure that each server is using a unique IP address, or configure each of the servers to obtain multicast addresses from a
Multicast Address Dynamic Client Allocation Protocol (MADCAP) server.
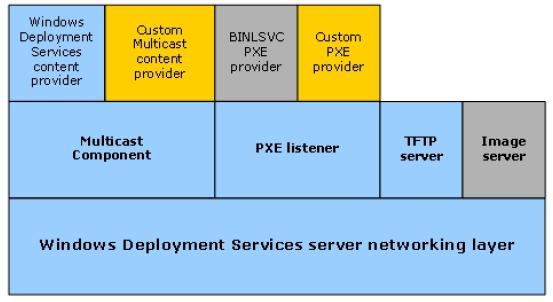
The server architectures are illustrated in the following diagram. The blue parts are installed with Transport Server and the Deployment Server. The grey parts are installed with the Deployment Server only. The yellow parts are not installed with either, but can be written using guidelines in the Windows SDK.
You need to recommend a security strategy for WebApp2 that meets the company's
Application requirements. What should you include in the recommendation?
- A. Basic authentication and connection security rules
- B. Basic authentication and SSL
- C. Digest authentication and connection security rules
- D. Digest authentication and SSL
Answer : B
You plan to deploy a distributed database Application that runs on multiple Windows Server
2008 R2 servers.
You need to design a storage strategy that meets the following requirements:
Allocates storage to servers as required
Uses the existing network infrastructure
Uses standard Windows management tools
Ensures that data is available if a single disk fails
What should you include in your design?
- A. An iSCSI disk storage subsystem that supports Microsoft Multipath I/O. Configure the storage subsystem as a RAID?0 array.
- B. An iSCSI disk storage subsystem that supports Virtual Disk Service (VDS). Configure the storage subsystem as a RAID?5 array.
- C. A Fibre Channel (FC) disk storage subsystem that supports Microsoft Multipath I/O. Configure the storage subsystem as a RAID?0 array.
- D. A Fibre Channel (FC) disk storage subsystem that supports the Virtual Disk Service (VDS). Configure the storage subsystem as a RAID?5 array.
Answer : B
Explanation:
MCITP Self-Paced Training Kit Exam 70-646 Windows Server Administration:
Virtual Disk Service (VDS)
Virtual Disk Service (VDS) provides a standard set of application programming interfaces
(APIs) that provide a single interface through which disks can be managed. VDS provides a complete solution for managing storage hardware and disks and enables you to create volumes on those disks. This means that you can use a single tool to manage devices in a mixed storage environment rather than tools provided by different hardware vendors.
Before you can manage a LUN using Storage Manager For SANs, you must install its VDS hardware provider. This will usually be provided by the hardware vendor. Prior to purchasing a storage device to be used on your organizations SAN, you should verify that a compatible VDS hardware provider exists.
VDS defines a software and a hardware provider interface. Each of these providers implements a different portion of the VDS API. The software provider is a program that runs on the host and is supported by a kernelmode driver. Software providers operate on volumes, disks, and partitions. The hardware provider manages the actual storage subsystem. Hardware providers are usually disk array or adapter cards that enable the creation of logical disks for each LUN type. The LUN type that can be configured will depend on the options allowed by the VDS hardware provider. For example, some VDS hardware providers will allow the RAID-5 (Striped with Parity) LUN type to be implemented, while others might be limited to providing the Mirrored or Spanned LUN types.
MORE INFO More on VDS -
For more information on the functionality of VDS, consult the following TechNet article:http://technet2.microsoft.com/windowsserver/en/library/dc77e7c7-ae44-4483-878b-
6bc3819e64dc1033.mspx?mfr=true
Storage Manager For SANs -
You can use the Storage Manager For SANs console to create LUNs on Fibre Channel and iSCSI storage arrays. You install Storage Manager For SANs as a Windows Server 2008 feature. To use Storage Manager
For SANs to manage LUNs, the following criteria must be met:
The storage subsystems that you are going to manage must support VDS.
The VDS hardware provider for each subsystem must already be installed on the Windows
Server 2008 computer. When you open Storage Manager For SANs from the
Administrative Tools menu, you are presented with three main nodes, which have the following functionality:
LUN ManagementThis node lists all of the LUNs created with Storage Manager For SANs.
From this node you can create new LUNs, extend the size of existing LUNs, assign and unassign LUNs, and delete LUNs. You can also use this node to configure the Fibre
Channel and iSCSI connections that servers use to access LUNs.
SubsystemsThis node lists all of the storage subsystems currently discovered within the
SAN environment. You can rename subsystems using this node.
DrivesThis node lists all of the drives in the storage subsystems discovered in the SA
Your company has a main office and a branch office. Your network contains a single Active
Directory domain.
The functional level of the domain is Windows Server 2008 R2. An Active Directory site exists for each office.
All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2. You plan to deploy file servers in each office.
You need to design a file sharing strategy to meet the following requirements:
-> Users in both offices must be able to access the same files.
-> Users in both offices must use the same Universal Naming Convention (UNC) path to access files.
-> The design must reduce the amount of bandwidth used to access files.
-> Users must be able to access files even if a server fails.
What should you include in your design?
- A. A standalone DFS namespace that uses replication.
- B. A domainbased DFS namespace that uses replication.
- C. A multisite failover cluster that contains a server located in the main office and another server located in the branch office.
- D. A Network Load Balancing cluster that contains a server located in the main office and another server located in the branch office.
Answer : B
Explanation:
MCITP Self-Paced Training Kit Exam 70-646 Windows Server Administration:
Domain-Based Namespaces -
You can create domain-based namespaces on one or more member servers or DCs in the same domain.
Metadata for a domain-based namespaces is stored by AD DS. Each server must contain an NTFS volume to host the namespace. Multiple namespace servers increase the availability of the namespace and ensure failover protection. A domain-based namespace cannot be a clustered resource in a failover cluster. However, you can locate the namespace on a server that is also a node in a failover cluster provided that you configure the namespace to use only local resources on that server. A domain-based namespace in
Windows Server -
2008 mode supports access-based enumeration. Windows Server 2008 mode is discussed later in this lesson.
You choose a domain-based namespace if you want to use multiple namespace servers to ensure the availability of the namespace, or if you want to make the name of the namespace server invisible to users.
When users do not need to know the UNC path to a namespace folder it is easier to replace the namespace server or migrate the namespace to another server.
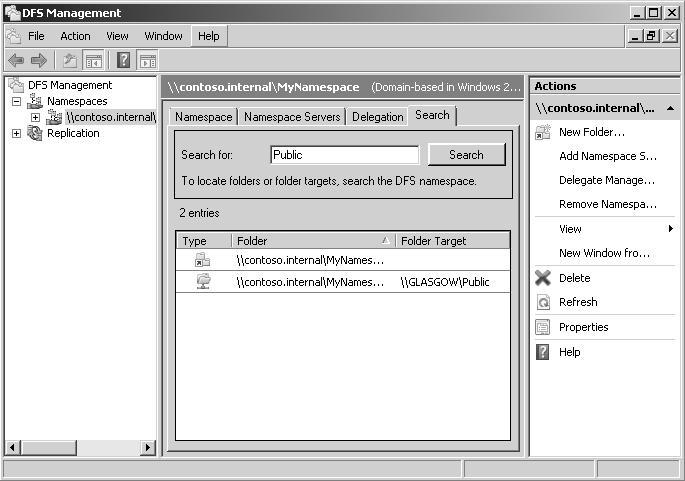
If, for example, a stand-alone namespace called \\Glasgow\Books needed to be transferred to a server called Brisbane, it would become \\Brisbane\Books. However, if it were a domain-based namespace (assuming Brisbane and Glasgow are both in the
Contoso.internal domain), it would be \\Contoso.internal\Books no matter which server hosted it, and it could be transferred from one server to the other without this transfer being apparent to the user, who would continue to use \\Contoso.internal\Books to access it.
Your company has a main office and three branch offices. The network consists of a single
Active Directory domain. Each office contains an Active Directory domain controller.
You need to create a DNS infrastructure for the network that meets the following requirements:
-> The DNS infrastructure must allow the client computers in each office to register
DNS names within their respective offices.
-> The client computers must be able to resolve names for hosts in all offices.
What should you do?
- A. Create an Active Directory-integrated zone at the main office site.
- B. Create a standard primary zone at the main office site and at each branch office site.
- C. Create a standard primary zone at the main office site. Create a secondary zone at each branch office site.
- D. Create a standard primary zone at the main office site. Create an Active Directory- integrated stub zone at each branch office site.
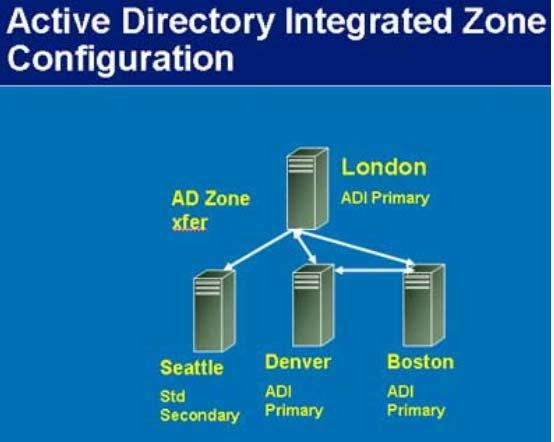
Answer : A
Explanation:
http://searchwindowsserver.techtarget.com/tip/DNS-Primer-Tips-for-understanding-Active-
Directory-integratedzone-design-and-configuration
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772101.aspx
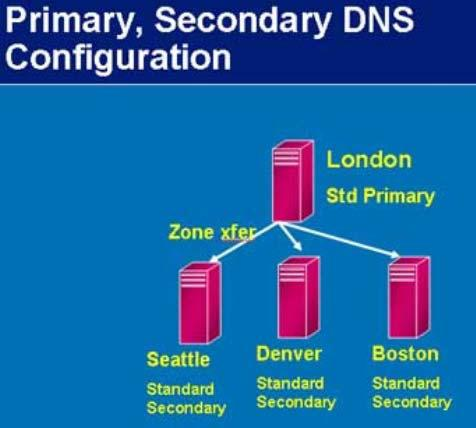
In an ADI primary zone, rather than keeping the old zone file on a disk, the DNS records are stored in the AD, and Active Directory replication is used rather than the old problematic zone transfer. If all DNS servers were to die or become inaccessible, you could simply install DNS on any domain controller (DC) in the domain. The records would be automatically populated and your DNS server would be up without the messy import/export tasks of standard DNS zone files.
Windows 2000 and 2003 allow you to put a standard secondary zone (read only) on a member server and use one of the ADI primary servers as the master.
When you decide which replication scope to choose, consider that the broader the replication scope, the greater the network traffic caused by replication. For example, if you decide to have AD DS-integrated DNS zone data replicated to all DNS servers in the forest, this will produce greater network traffic than replicating the DNS zone data to all DNS servers in a single AD DS domain in that forest.
AD DS-integrated DNS zone data that is stored in an application directory partition is not replicated to the global catalog for the forest. The domain controller that contains the global catalog can also host application directory partitions, but it will not replicate this data to its global catalog.
AD DS-integrated DNS zone data that is stored in a domain partition is replicated to all domain controllers in its AD DS domain, and a portion of this data is stored in the global catalog. This setting is used to support Windows 2000.
If an application directory partition's replication scope replicates across AD DS sites, replication will occur with the same intersite replication schedule as is used for domain partition data.
By default, the Net Logon service registers domain controller locator (Locator) DNS resource records for the application directory partitions that are hosted on a domain controller in the same manner as it registers domain controller locator (Locator) DNS resource records for the domain partition that is hosted on a domain controller.

