Your network consists of an Active Directory forest that contains two domains. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2. All domain controllers are configured as DNS Servers.
You have a standard primary zone for dev.contoso.com that is stored on a member server.
You need to ensure that all domain controllers can resolve names from the dev.contoso.com zone.
What should you do?
- A. On the member server, create a stub zone.
- B. On the member server, create a NS record for each domain controller.
- C. On one domain controller, create a conditional forwarder. Configure the conditional forwarder to replicate to all DNS servers in the forest.
- D. On one domain controller, create a conditional forwarder. Configure the conditional forwarder to replicate to all DNS servers in the domain.
Answer : C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc730756.aspx
Understanding Forwarders -
A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that forwards DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders.
You designate a DNS server on a network as a forwarder by configuring the other DNS servers in the network to forward the queries that they cannot resolve locally to that DNS server. By using a forwarder, you can manage name resolution for names outside your network, such as names on the Internet, and improve the efficiency of name resolution for the computers in your network.
The following figure illustrates how external name queries are directed with forwarders.
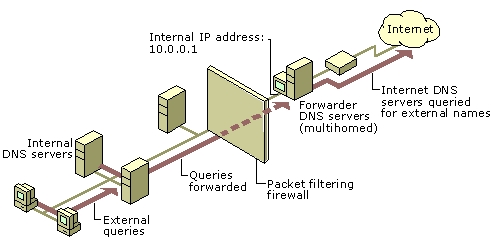
C:\Documents and Settings\usernwz1\Desktop\1.PNG
Conditional forwarders -
A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that forwards DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, you can configure a DNS server to forward all the queries that it receives for names ending with corp.contoso.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers.
Further information:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794735%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Assign a Conditional Forwarder for a Domain Name
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx
Configure a DNS Server to Use Forwarders
Your company has an Active Directory forest. The company has servers that run Windows
Server 2008 R2 and client computers that run Windows 7. The domain uses a set of GPO administrative templates that have been approved to support regulatory compliance requirements.
Your partner company has an Active Directory forest that contains a single domain. The company has servers that run Windows Server 2008 R2 and client computers that run
Windows 7.
You need to configure your partner company's domain to use the approved set of administrative templates.
What should you do?
- A. Use the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) utility to back up the GPO to a file. In each site, import the GPO to the default domain policy.
- B. Copy the ADMX files from your company's PDC emulator to the PolicyDefinitions folder on the partner company's PDC emulator.
- C. Copy the ADML files from your company's PDC emulator to the PolicyDefinitions folder on the partner company's PDC emulator.
- D. Download the conf.adm, system.adm, wuau.adm, and inetres.adm files from the Microsoft Updates Web site. Copy the ADM files to the PolicyDefinitions folder on thr partner company's emulator.
Answer : B
Explanation:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/929841
How to create the Central Store for Group Policy Administrative Template files in Windows
Vista Windows Vista uses a new format to display registry-based policy settings. These registry-based policy settings appear under Administrative Templates in the Group Policy
Object Editor. In Windows Vista, these registry-based policy settings are defined by standards-based XML files that have an .admx file name extension. The .admx file format replaces the legacy .adm file format. The .adm file format uses a proprietary markup language.
In Windows Vista, Administrative Template files are divided into .admx files and language- specific .adml files that are available to Group Policy administrators.
Administrative Template file storage
In earlier operating systems, all the default Administrative Template files are added to the
ADM folder of a Group Policy object (GPO) on a domain controller. The GPOs are stored in the SYSVOL folder. The SYSVOL folder is automatically replicated to other domain controllers in the same domain. A policy file uses approximately 2 megabytes (MB) of hard disk space. Because each domain controller stores a distinct version of a policy, replication traffic is increased.
Windows Vista uses a Central Store to store Administrative Template files. In Windows
Vista, the ADM folder is not created in a GPO as in earlier versions of Windows. Therefore, domain controllers do not store or replicate redundant copies of .adm files.
The Central Store -
To take advantage of the benefits of .admx files, you must create a Central Store in the
SYSVOL folder on a domain controller. The Central Store is a file location that is checked by the Group Policy tools. The Group Policy tools use any .admx files that are in the
Central Store. The files that are in the Central Store are later replicated to all domain controllers in the domain.
To create a Central Store for .admx and .adml files, create a folder that is named
PolicyDefinitions in the following location:
\\FQDN\SYSVOL\FQDN\policies
Note: FQDN is a fully qualified domain name.
http://www.frickelsoft.net/blog/?p=31
How can I export local Group Policy settings made in gpedit.msc?
Mark Heitbrink, MVP for Group Policy came up with a good solution on how you can export the Group
Policy and Security settings you made in on a machine with the Local Group Policy
Editor (gpedit.msc) to other machines pretty easy:
Normal settings can be copied like this:
1.) Open %systemroot%\system32\grouppolicy\
Within this folder, there are two folders - machine and user. Copy these to folders to the
%systemroot%
\system32\grouppolicy - folder on the target machine. All it needs now is a reboot or a gpupdate /force.
Note: If you cannot see the grouppolicy folder on either the source or the target machine, be sure to have your explorer folder options set to Show hidden files and folders
For security settings:
1.) Open MMC and add the Snapin Security Templates.
2.) Create y
Your company has file servers located in an organizational unit named Payroll. The file servers contain payroll files located in a folder named Payroll.
You create a GPO.
You need to track which employees access the Payroll files on the file servers.
What should you do?
- A. Enable the Audit process tracking option. Link the GPO to the Domain Controllers organizational unit. On the file servers, configure Auditing for the Authenticated Users group in the Payroll folder.
- B. Enable the Audit object access option. Link the GPO to the Payroll organizational unit. On the file servers, configure Auditing for the Everyone group in the Payroll folder.
- C. Enable the Audit process tracking option. Link the GPO to the Payroll organizational unit. On the file servers, configure Auditing for the Everyone group in the Payroll folder.
- D. Enable the Audit object access option. Link the GPO to the domain. On the domain controllers, configure Auditing for the Authenticated Users group in the Payroll folder.
Answer : B
Explanation:
Answer: Enable the Audit object access option. Link the GPO to the Payroll organizational unit. On the file servers, configure Auditing for the Everyone group in the Payroll folder. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd349800%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Audit Policy -
Establishing an organizational computer system audit policy is an important facet of information security.
Configuring Audit policy settings that monitor the creation or modification of objects gives you a way to track potential security problems, helps to ensure user accountability, and provides evidence in the event of a security breach.
There are nine different kinds of events for which you can specify Audit Policy settings. If you audit any of these kinds of events, Windows records the events in the Security log, which you can find in Event Viewer.
Object access. Audit this to record when someone has used a file, folder, printer, or other object.
Process tracking. Audit this to record when events such as program activation or a process exiting occur.
When you implement Audit Policy settings:
If you want to audit directory service access or object access, determine which objects you want to audit access of and what type of access you want to audit. For example, if you want to audit all attempts by users to open a particular file, you can configure audit policy settings in the object access event category so that both successful and failed attempts to read a file are recorded.
Further information:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh147307%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Group Policy for Beginners -
Group Policy Links -
At the top level of AD DS are sites and domains. Simple implementations will have a single site and a single domain. Within a domain, you can create organizational units (OUs). OUs are like folders in Windows Explorer.
Instead of containing files and subfolders, however, they can contain computers, users, and other objects.
For example, in Figure 1 you see an OU named Departments. Below the Departments OU, you see four subfolders: Accounting, Engineering, Management, and Marketing. These are child OUs. Other than the
Domain Controllers OU that you see in Figure 1, nothing else in the figure is an OU.
What does this have to do with Group Policy links? Well, GPOs in the Group Policy objects folder have no impact unless you link them to a site, domain, or OU. When you link a GPO to a container, Group Policy applies the GPOs settings to the computers and users in that container.
You need to remove the Active Directory Domain Services role from a domain controller named DC1.
What should you do?
- A. Run the netdom remove DC1 command.
- B. Run the Dcpromo utility. Remove the Active Directory Domain Services role.
- C. Run the nltest /remove_server: DC1 command.
- D. Reset the Domain Controller computer account by using the Active Directory Users and Computers utility.
Answer : B
Explanation:
Answer: Run the Dcpromo utility. Remove the Active Directory Domain Services role. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771844%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Removing a Domain Controller from a Domain
To remove a domain controller by using the Windows interface
1. Click Start, click Run, type dcpromo, and then press ENTER.
Further information:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772217%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Netdom -
Enables administrators to manage Active Directory domains and trust relationships from the command prompt.
Netdom is a command-line tool that is built into Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server
2008 R2. It is available if you have the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) server role installed. It is also available if you install the Active Directory Domain Services Tools that are part of the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
Commands -
Netdom remove -
Removes a workstation or server from the domain.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731935%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Nltest Performs network administrative tasks.
Nltest is a command-line tool that is built into Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server
2008 R2. It is available if you have the AD DS or the AD LDS server role installed. It is also available if you install the Active
Directory Domain Services Tools that are part of the Remote Server Administration Tools
(RSAT).
You can use nltest to:
Get a list of domain controllers
Force a remote shutdown -
Query the status of trust -
Test trust relationships and the state of domain controller replication in a Windows domain
Force a user-account database to synchronize on Windows NT version 4.0 or earlier domain controllers
Personal comment #1:
There is no /remove_server switch for the nltest command
Personal comment #2:
Resetting the Domain Controller's computer account has nothing to do with this question
You have an Active Directory domain that runs Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to implement a certification authority (CA) server that meets the following requirements:
Allows the certification authority to automatically issue certificates
Integrates with Active Directory Domain Services
What should you do?
- A. Install and configure the Active Directory Certificate Services server role as a Standalone Root CA.
- B. Install and configure the Active Directory Certificate Services server role as an Enterprise Root CA.
- C. Purchase a certificate from a third-party certification authority, Install and configure the Active Directory Certificate Services server role as a Standalone Subordinate CA.
- D. Purchase a certificate from a third-party certification authority, Import the certificate into the computer store of the schema master.
Answer : B
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc776874%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Enterprise certification authorities
The Enterprise Administrator can install Certificate Services to create an enterprise certification authority (CA).
Enterprise CAs can issue certificates for purposes such as digital signatures, secure e-mail using S/MIME
(Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions), authentication to a secure Web server using Secure Sockets
Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) and logging on to a Windows Server 2003 family domain using a smart card.
An enterprise CA has the following features:
An enterprise CA requires the Active Directory directory service.
When you install an enterprise root CA, it uses Group Policy to propagate its certificate to the Trusted
Root Certification Authorities certificate store for all users and computers in the domain.
You must be a -
Domain Administrator or be an administrator with write access to Active Directory to install an enterprise root
CA.
Certificates can be issued for logging on to a Windows Server 2003 family domain using smart cards.
The enterprise exit module publishes user certificates and the certificate revocation list
(CRL) to Active
Directory. In order to publish certificates to Active Directory, the server that the CA is installed on must be a member of the Certificate Publishers group. This is automatic for the domain the server is in, but the server must be delegated the proper security permissions to publish certificates in other domains.
For more -
information about the exit module, see Policy and exit modules.
An enterprise CA uses certificate types, which are based on a certificate template. The following functionality is possible when you use certificate templates:
Enterprise CAs enforce credential checks on users during certificate enrollment. Each certificate template has a security permission set in Active Directory that determines whether the certificate requester is authorized to receive the type of certificate they have requested.
The certificate subject name can be generated automatically from the information in Active
Directory or -
supplied explicitly by the requestor.
The policy module adds a predefined list of certificate extensions to the issued certificate.
The extensions -
are defined by the certificate template. This reduces the amount of information a certificate requester has to provide about the certificate and its intended use. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc780501%28WS.10%29.aspx
Stand-alone certification authorities
You can install Certificate Services to create a stand-alone certification authority (CA).
Stand-alone CAs can -
issue certificates for purposes such as digital signatures, secure e-mail using S/MIME
(Secure Multipurpose
Internet Mail Extensions) and authentication to a secure Web server using Secure Sockets
Layer (SSL) or -
Transport Layer Security (TLS).
A stand-alone CA has the following characteristics:
Unlike an enterprise CA, a stand-

